Recent Articles
-

Performance Enhancement of Human Activity Recognition Using Millimeter-Wave Multi-Link Channels
28 November 2025 Yupeng Wang, Jiming Lv, Keisuke Wako and Minseok Kim propose a multi-vantage sensing framework that employs two bistatic configurations of mmWave multi-link channel measurements, positioned at the anterior and posterior sides of a human subject. Doppler spectrograms obtained from both perspectives are fused to leverage the diverse motion features captured from each viewpoint. A convolutional neural network (CNN) was trained on the fused spectrograms, and six widely adopted CNN architectures were evaluated to determine the most effective configuration. To further improve classification accuracy, we also developed a hybrid approach that combines CNN-based feature extraction with a support vector machine (SVM) classifier.
-
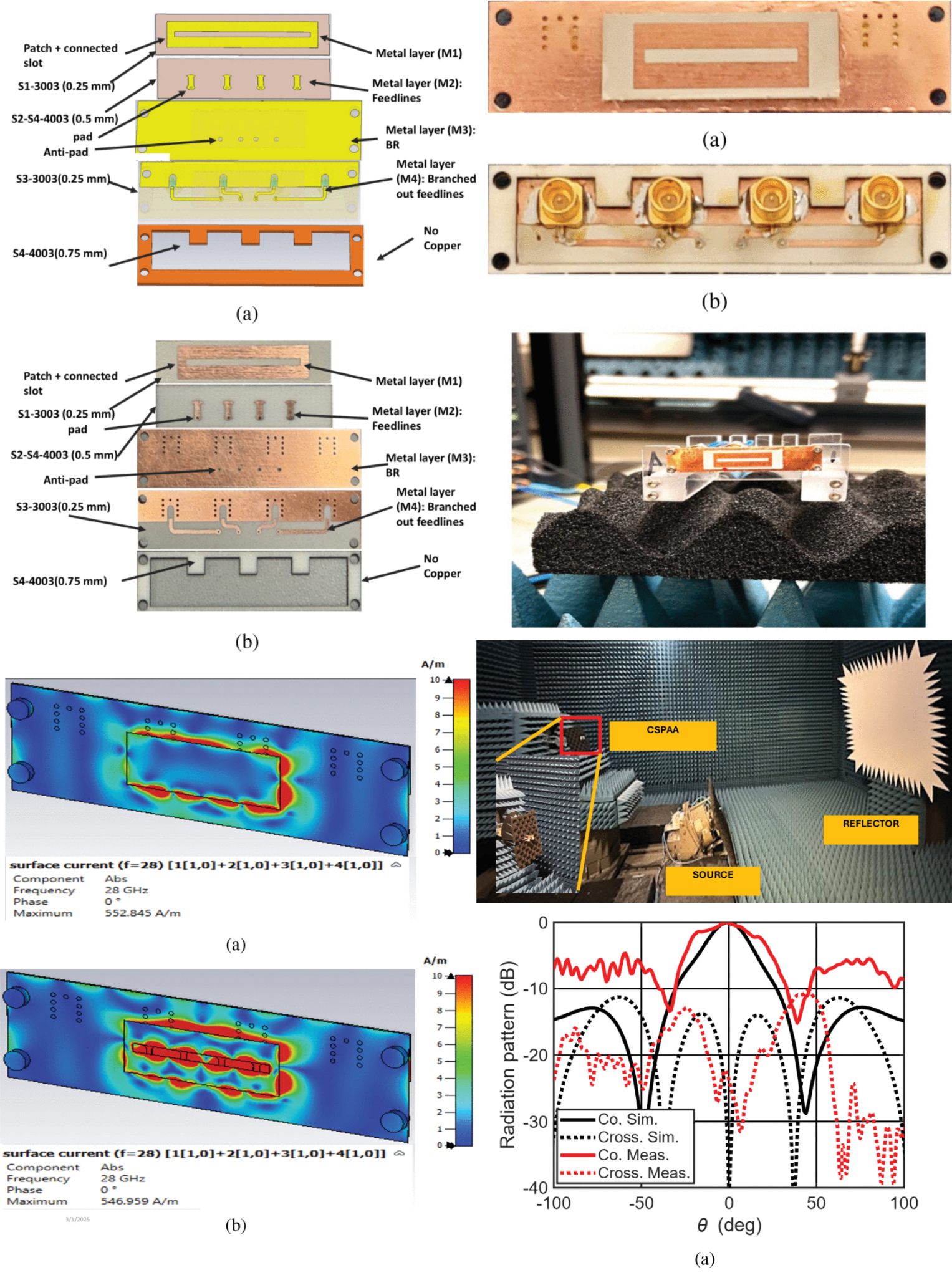
Wideband, Beamsteerable Connected Slotted-Patch Antenna Array for On-Package Millimeter Wave Applications
28 November 2025 Md Rasheduzzaman Al-Amin, Elham Baladi and Mohammad S. Sharawi propose connected slotted-patch antenna array (CSPAA) is designed, analyzed, fabricated, and measured for on-package millimeter-wave (mmWave) applications having wide beamsteering capabilities. Microstrip lines are used to excite the patch and the connected slot. The CSPAA is designed on a seven-layer vertical stack-up, making it suitable for on-package scenarios. The fabricated CSPAA has a measured bandwidth of 21.07% (centered at 28 GHz) and a measured realized gain of 9.51 dBi at broadside, yielding a total efficiency of 83%.
-
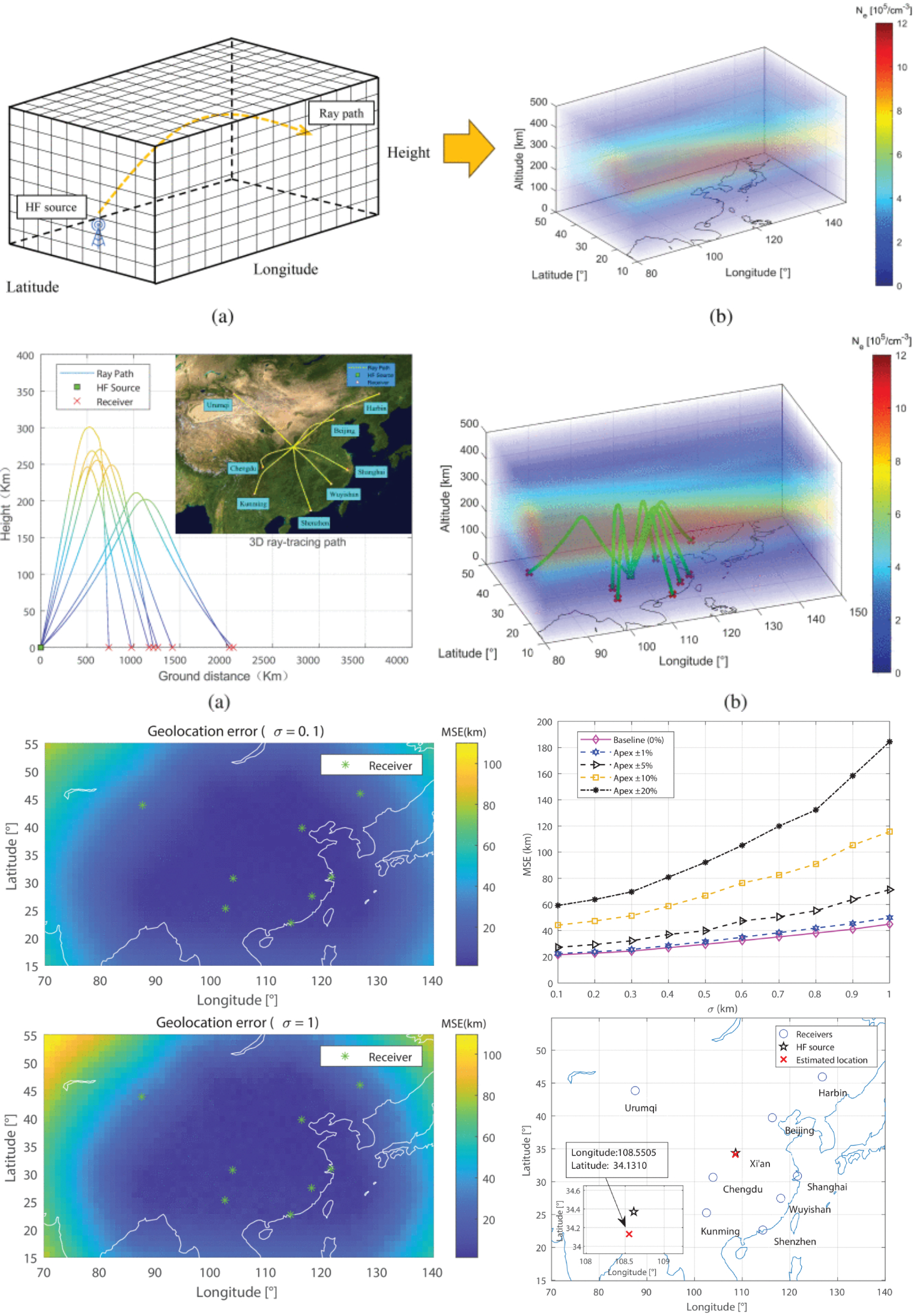
An Adaptive Sensor Selection and Ray-Tracing-Assisted TDOA Method for HF Skywave Source Geolocation With Experimental Validation
28 November 2025 Chen Xu, Houlong Ai, Hao Zhao, Zhaoyang Li and Xijun Liu propose an enhanced geolocation framework based on Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA) and semidefinite programming (SDP) to accurately estimate HF skywave source positions using geographically distributed receivers. They construct a three-dimensional (3D) ionospheric plasma density grid matrix model by combining an improved wideband ionospheric channel model with a ray-tracing technique. This model not only generates simulated TDOA data but also provides essential prior ionospheric information for real-world geolocation.
-
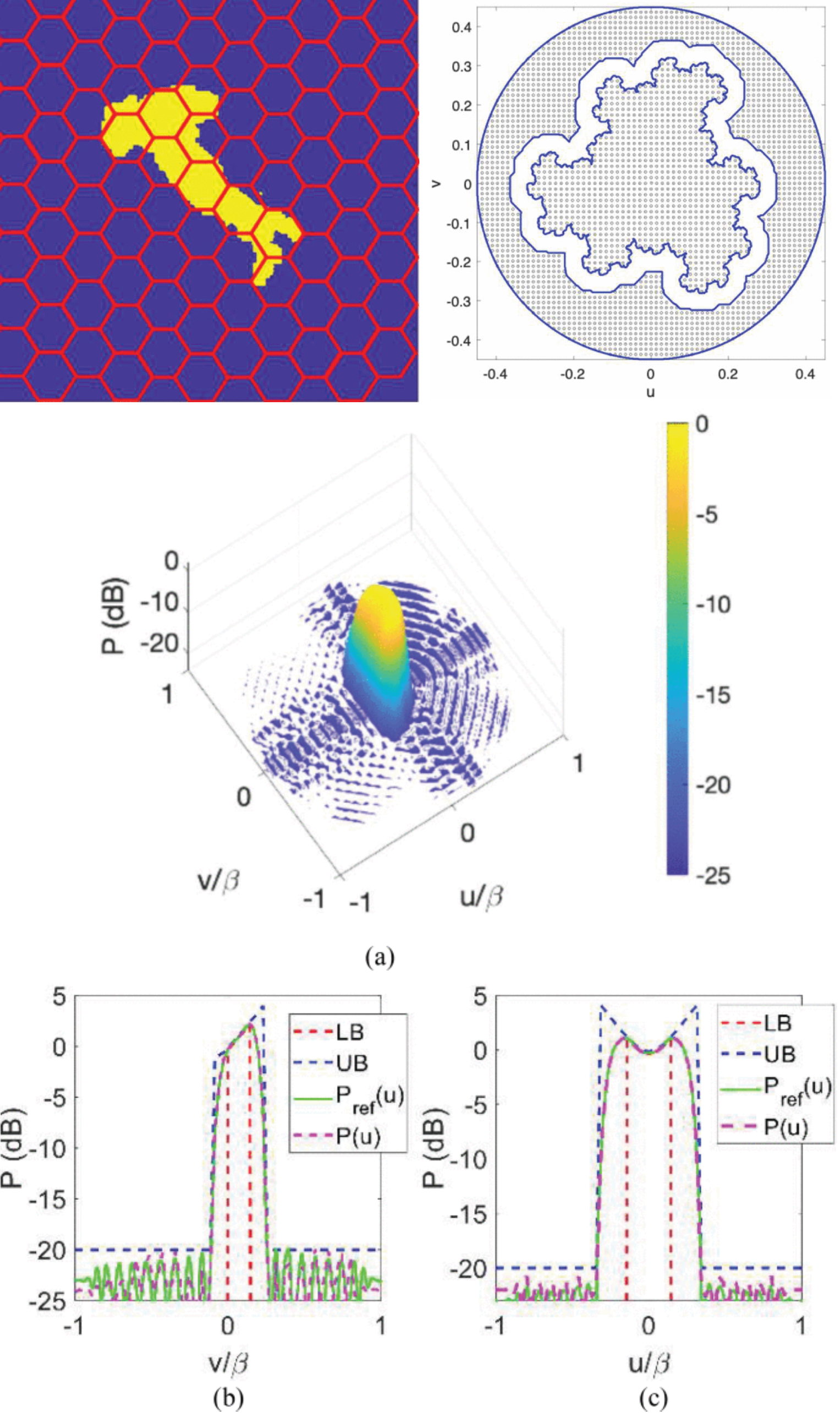
Minimal-Size 2-D Sources for Mask-Constrained Synthesis of Shaped Patterns
26 November 2025 Giada M. Battaglia, Andrea F. Morabito, Roberta Palmeri and Tommaso Isernia provide an effective deterministic solution to the canonical and, until now, unsolved problem of the optimal synthesis of 2-D mask-constrained shaped beams. In particular, for 2-D arrays on planar grids and continuous aperture sources with circular support, we identify the minimum source size required to achieve a given mask-constrained performance and, subsequently, synthesize such a source. Conversely, the proposed method can also determine and achieve the optimal performance attainable by a source of fixed size. The approach, based solely on convex programming and polynomial factorization, can accommodate completely arbitrary upper and lower bounds on the radiated power pattern.
-
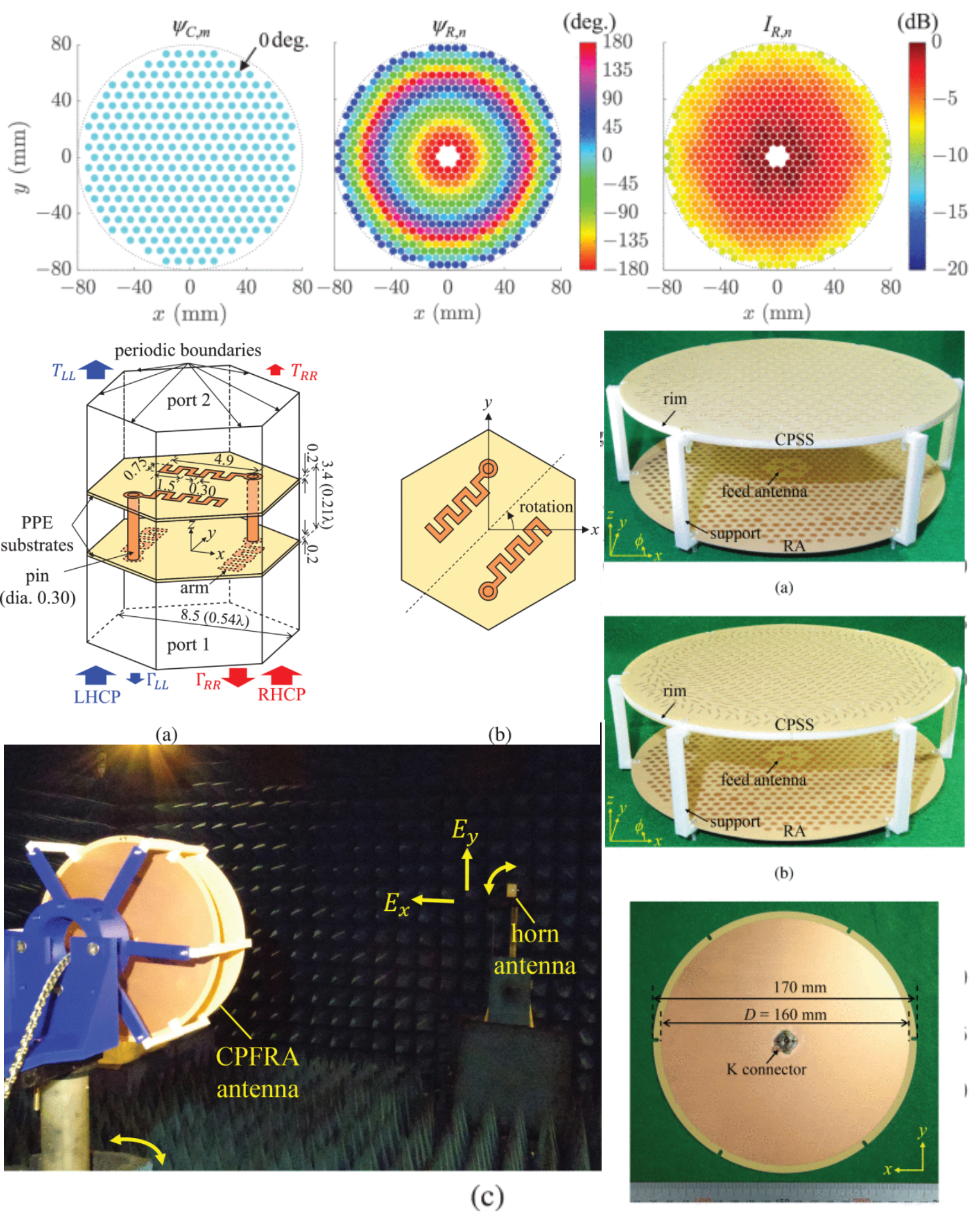
Circularly Polarized Folded Reflectarray Antenna With Improved Aperture Efficiency
18 November 2025 Makoto Sano presents a method for improving the aperture efficiency of circularly polarized folded reflectarray (CPFRA) antennas. The reflection-phase distribution of the circular polarization selective surface (CPSS) constituting the CPFRA antenna is modified to maximize the aperture efficiency. CPFRA antennas designed with the proposed and conventional methods are simulated. Compared with the conventional CPFRA antenna with uniform CPSS reflection-phase distribution, the proposed one with the optimized non-uniform distribution has less spillover and higher aperture efficiency. The directivity and the corresponding aperture efficiency of the proposed CPFRA antenna are 28.7 dBic and 72.7% at 18.95 GHz, respectively.antenna.
-
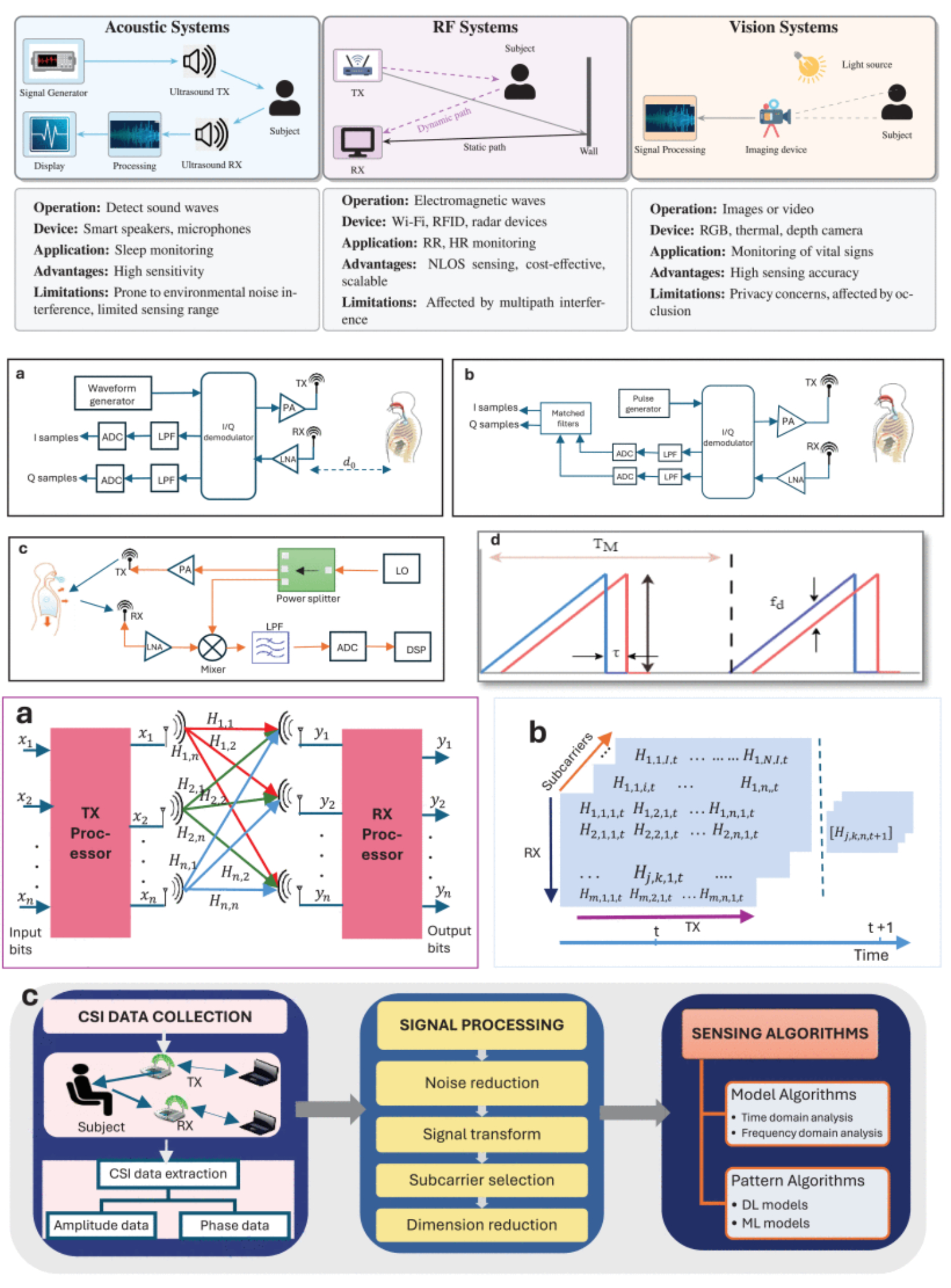
Non-Invasive Vital Signs Sensing: Advances, Challenges, and Future Directions in Radio Frequency Based Techniques
12 November 2025 Prisila Ishabakaki, Hira Hameed, Muhammad Farooq, Michael S. Mollel, Hasan Abbas, Muhammad A. Imran and Qammer H. Abbasi delves into the principles and performance of state-of-the-art RF-based monitoring systems. Significant advances in signal processing techniques and machine learning (ML) models have markedly improved the accuracy and reliability of vital signs detection. These innovations underscore the potential of RF technologies to redefine healthcare monitoring. This review provides a comprehensive understanding of the operational mechanisms underlying RF-based monitoring systems and proposes improvements to overcome current barriers, thereby advancing the field of non-invasive vital signs monitoring and broadening its application in healthcare.
-
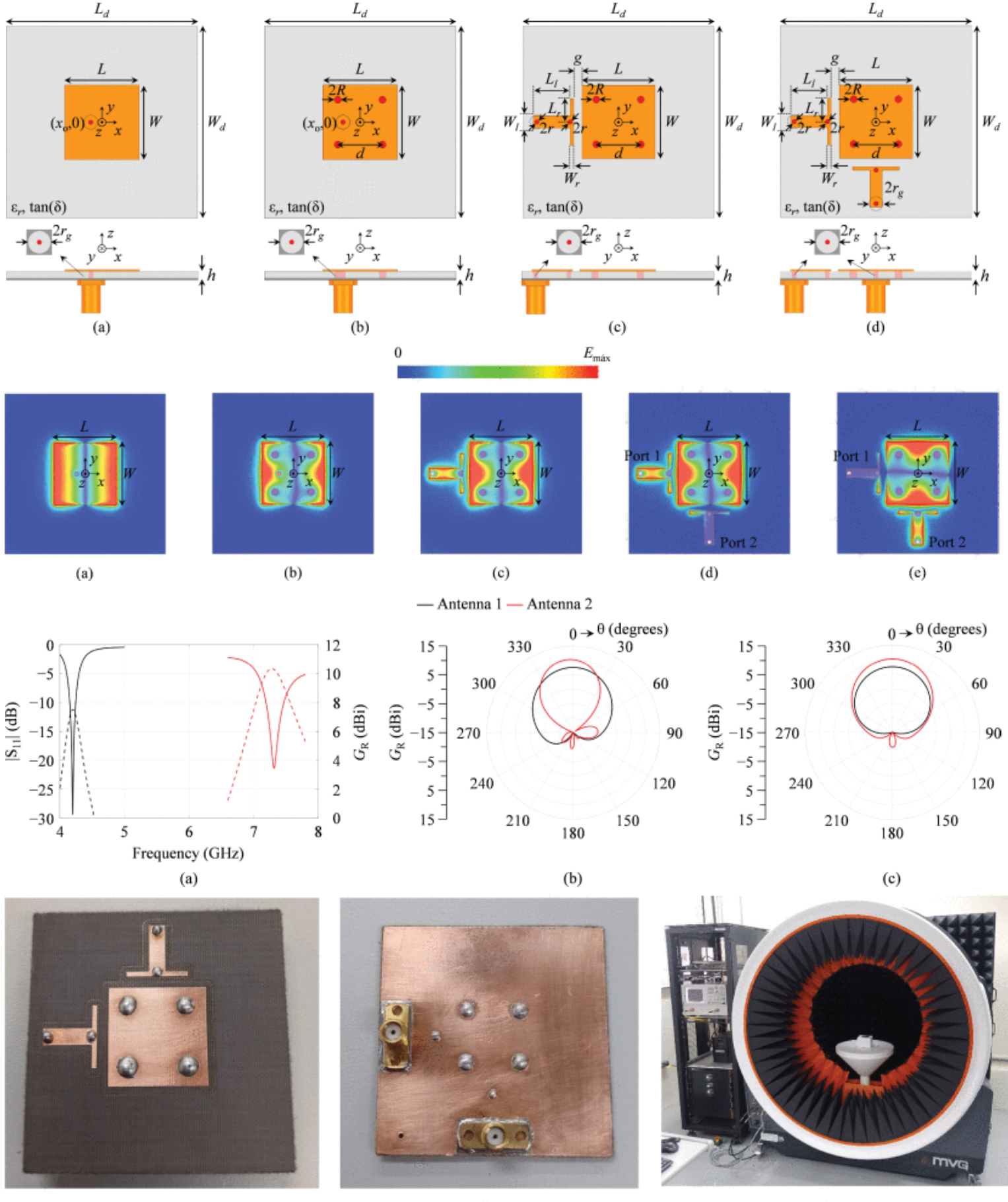
Dual-Polarized Microstrip Patch Antenna With Enhanced Bandwidth and Gain Using Mode Perturbation and λ/4 Resonator Coupling
11 November 2025 Renan A. Santos, Natanael M. L. Sousa, Ildefonso Bianchi, Manish Sharma, Rafael A. Penchel and Daniel C. Nascimento propose a dual-polarized (DP) square microstrip patch antenna (MPA) with enhanced bandwidth and gain. The antenna operates in modified TM10/TM01-like modes, excited independently via two orthogonal ports, and enabled by four symmetrically placed metallic vias that perturb the field distribution within the substrate. As a result, the antenna becomes electrically larger relative to the wavelength at resonance frequency, leading to an increase in realized gain. To enhance the bandwidth, the proposed MPA is fed by a pair of quarter-wavelength microstrip line resonators, which introduce an additional resonance associated with the feeding structure, and function as an integrated filter.
-
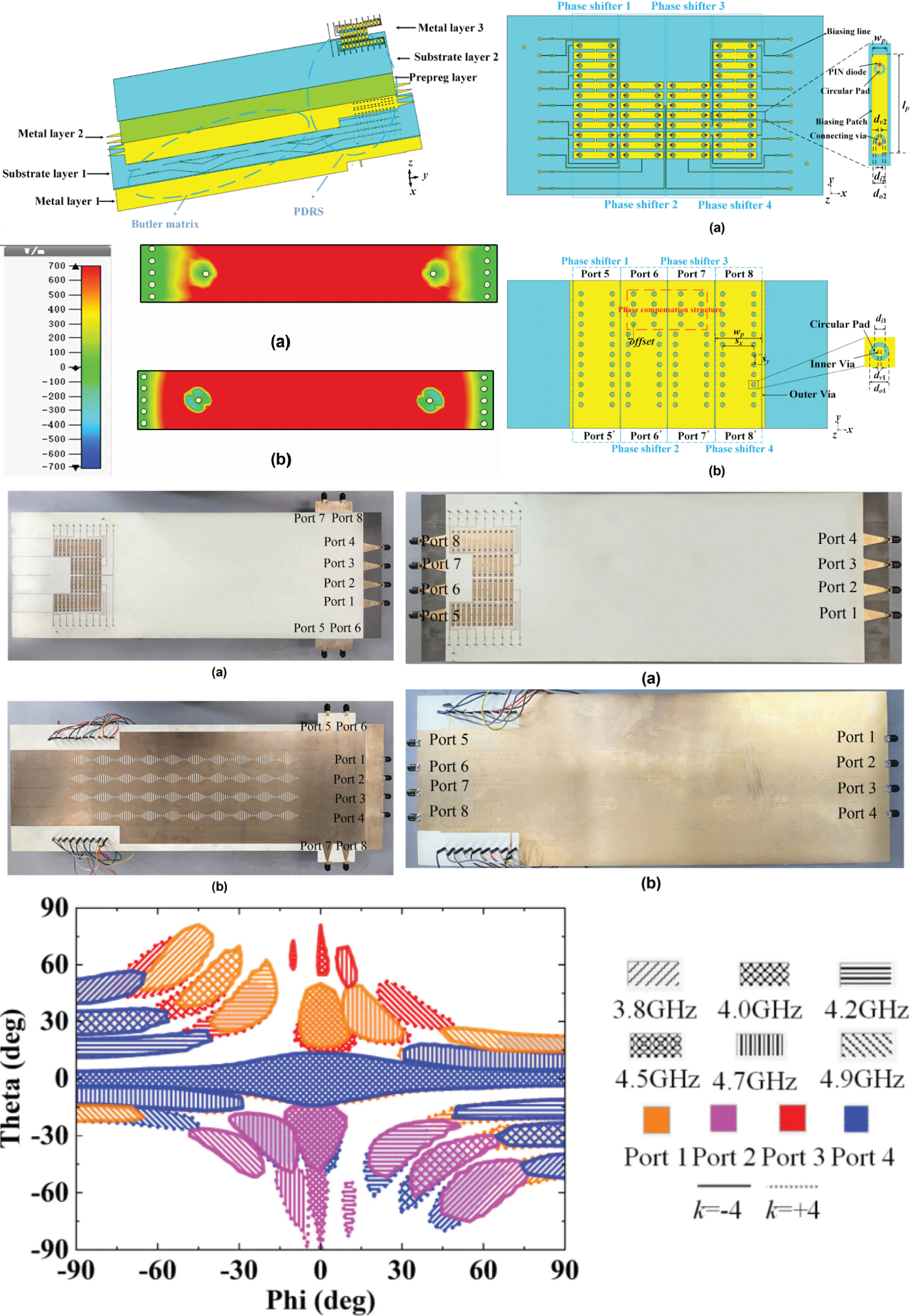
High Resolution Beam-Scanning Leaky-Wave Antenna Array With Phase Difference Reconfigurable Structure Cascaded Butler Matrix
10 November 2025 Xingyu Pang, Yunjie Geng and Junhong Wang present a leaky-wave antenna (LWA) array with high resolution beam scanning capability in two dimensions (2D) The antenna array is fed by a substrate integrated waveguide (SIW) Butler matrix cascaded with a phase difference reconfigurable structure (PDRS). By activating different states of the PDRS, the number of phase difference sets at the output ports of the Butler matrix increases from 4 to 36, achieving an 11.25° phase resolution. Prototype of the feeding network was first fabricated and measured, the results show that the phase difference range is extended to –180° to 180°, with an imbalance of ±20° over 3.9-4.7 GHz. The 2D beam-scanning LWA array prototype was also fabricated and measured.
-
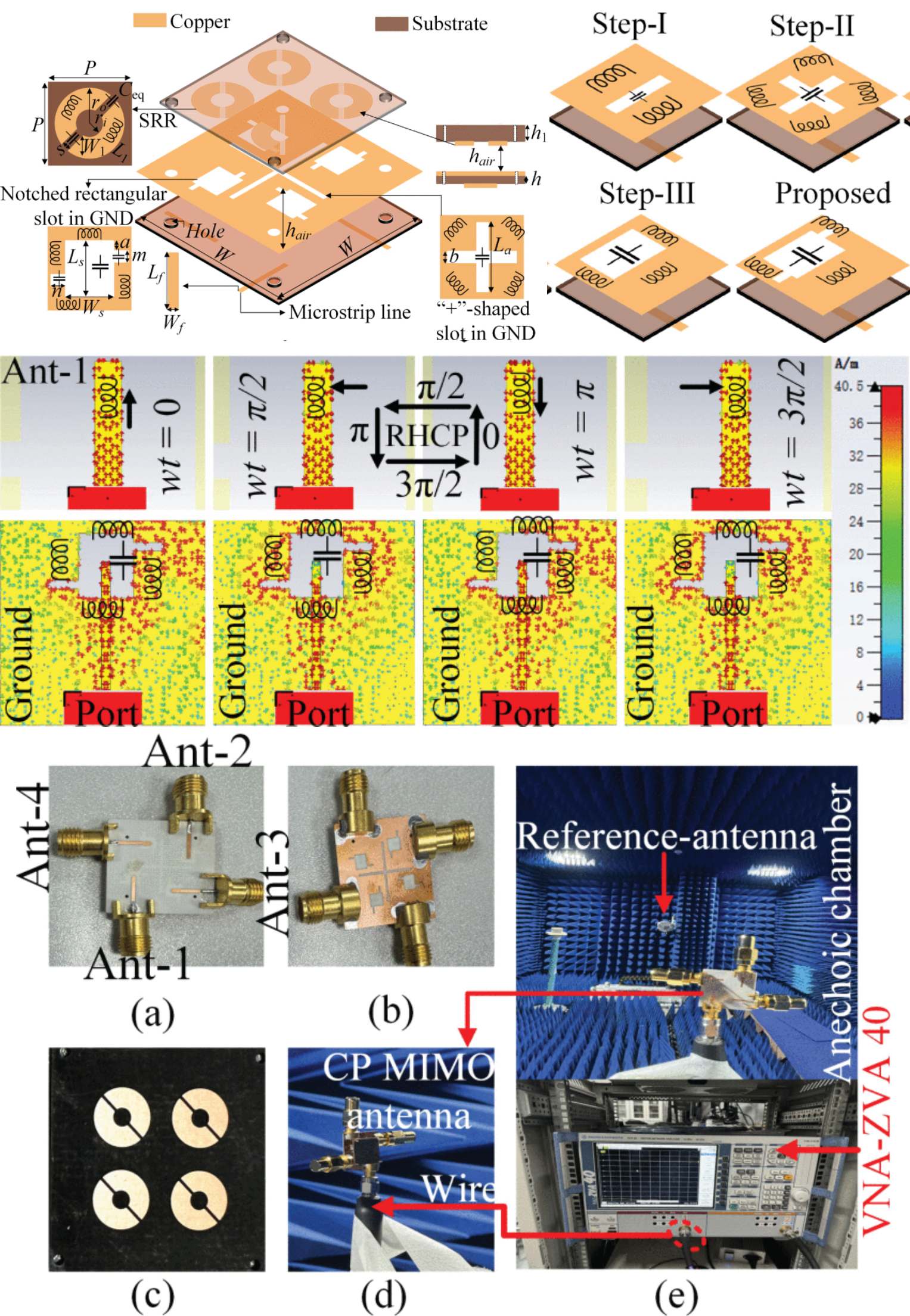
A Miniaturized Quad-Port Circularly Polarized MIMO Antenna for mmWave Wireless Applications
10 November 2025 Abdul Majeed, Yejun He and Yi Huang present a miniaturized quad-port circularly polarized (CP) multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) slot antenna with enhanced isolation, gain, and diversity performance for millimeter-wave (mmWave) applications. Each port excites an identical notched rectangular slot via a 50 Ω microstrip line. A simple “+”-shaped slot etched on the ground plane improves inter-element isolation. Additionally, a split ring resonator (SRR)-based reflector, designed at the antenna’s fundamental mode and placed above the array, improves the gain by 1 dBic and further reduces mutual coupling within a compact size of 14×14×0 .508 mm3 ( 1.31λ0×1.31λ0×0.047λ0 ), where λ0 is free space wavelength at the operating frequency of 28 GHz.
-
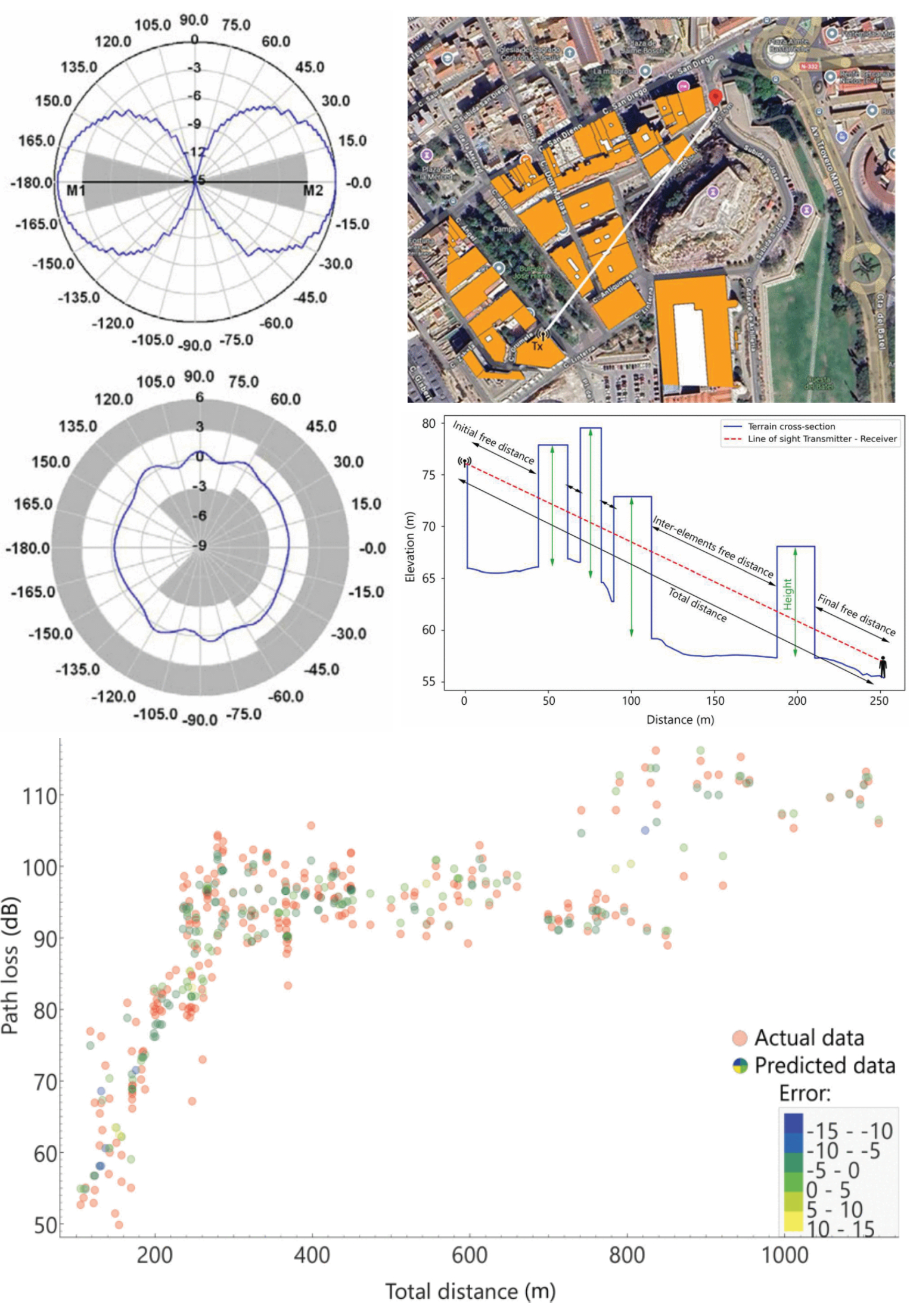
Machine-Learning-Based Urban Path Loss Prediction at 900 MHz: Principal Component Analysis, Clustering, Feature Importance and Regression
07 November 2025 José Lorente-López, Ignacio Rodríguez-Rodríguez, José-Víctor Rodríguez, Jose María Molina García-Pardo and Juan Aznar-Poveda explore the possibility of applying machine learning (ML) techniques to analyze and predict radio wave propagation losses in urban environments. Thus, from a measurement campaign–conducted at 900 MHz in Cartagena, Spain– and the obtaining, by means of digital terrain and cadastral maps, of a series of relevant geospatial variables, urban path loss is analyzed through clustering methods and principal component analysis (PCA), as well as predicted using multivariate ML-based regression models. A feature importance analysis is also carried out to identify key independent variables (predictors) which can be crucial for improved path loss prediction. radome of arbitrary shape.

















